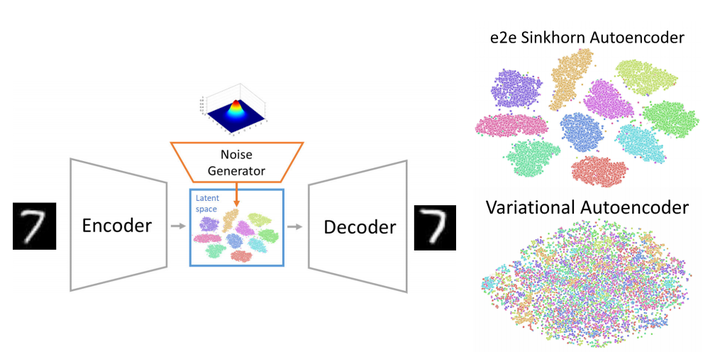
 Schematic visualisation of end-to-end Sinkhorn Autoencoder processing (left). TSNE visualisation of latent space for MNIST dataset (right). Our conditional e2e Sinkhorn Autoencoder (top) and conditional VAE (bottom). Our model does not restrict latent space to the normal distribution, therefore classes may be even linearly separable.
Schematic visualisation of end-to-end Sinkhorn Autoencoder processing (left). TSNE visualisation of latent space for MNIST dataset (right). Our conditional e2e Sinkhorn Autoencoder (top) and conditional VAE (bottom). Our model does not restrict latent space to the normal distribution, therefore classes may be even linearly separable.
Abstract
In this work, we propose a novel end-to-end Sinkhorn Autoencoder with a noise generator for efficient data collection simulation. Simulating processes that aim at collecting experimental data is crucial for multiple real-life applications, including nuclear medicine, astronomy, and high energy physics. Contemporary methods, such as Monte Carlo algorithms, provide high-fidelity results at a price of high computational cost. Multiple attempts are taken to reduce this burden, e.g. using generative approaches based on Generative Adversarial Networks or Variational Autoencoders. Although such methods are much faster, they are often unstable in training and do not allow sampling from an entire data distribution. To address these shortcomings, we introduce a novel method dubbed end-to-end Sinkhorn Autoencoder, that leverages the Sinkhorn algorithm to explicitly align distribution of encoded real data examples and generated noise. More precisely, we extend autoencoder architecture by adding a deterministic neural network trained to map noise from a known distribution onto autoencoder latent space representing data distribution. We optimise the entire model jointly. Our method outperforms co mpeting approaches on a challenging dataset of simulation data from Zero Degree Calorimeters of ALICE experiment in LHC. as well as standard benchmarks, such as MNIST and CelebA.